




Centre Of Excellence
Dr. G. Ramesh contributes remarkable clinical depth across our Centers of Excellence, strengthening our role in Super Speciality Tertiary Healthcare.
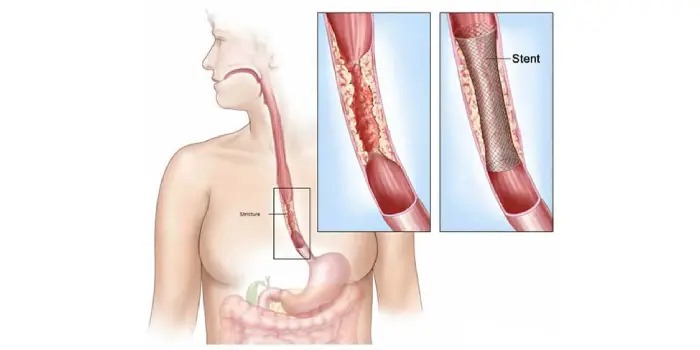
Strictures Dilation
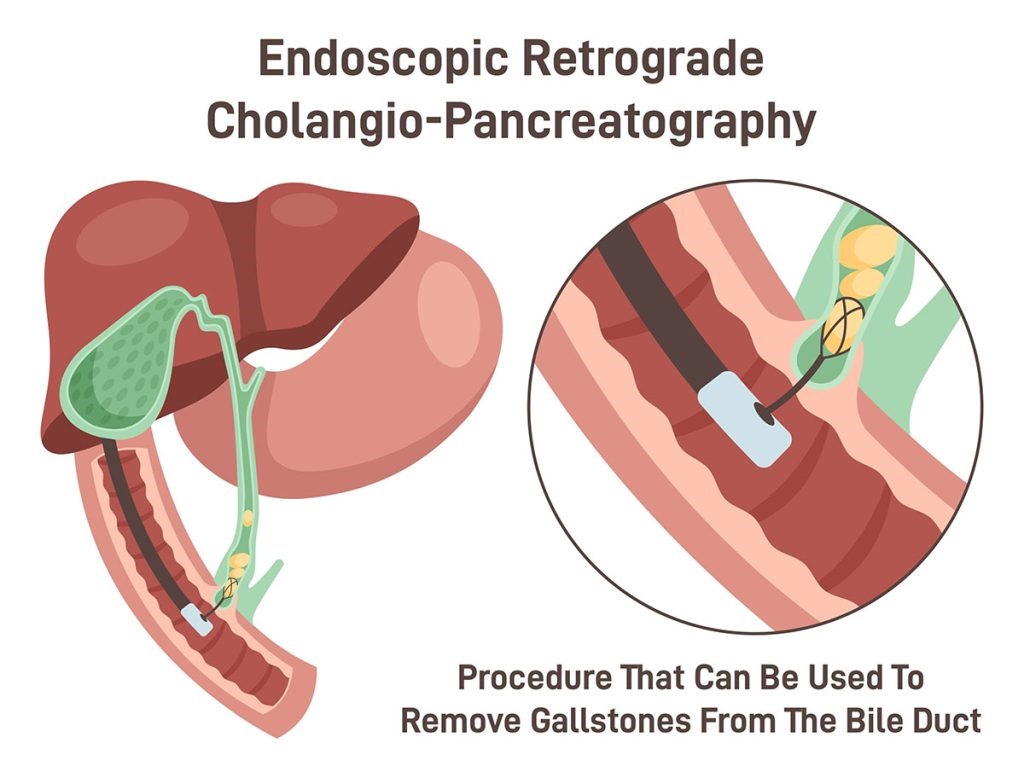
ERCP - CBD Stone Removal
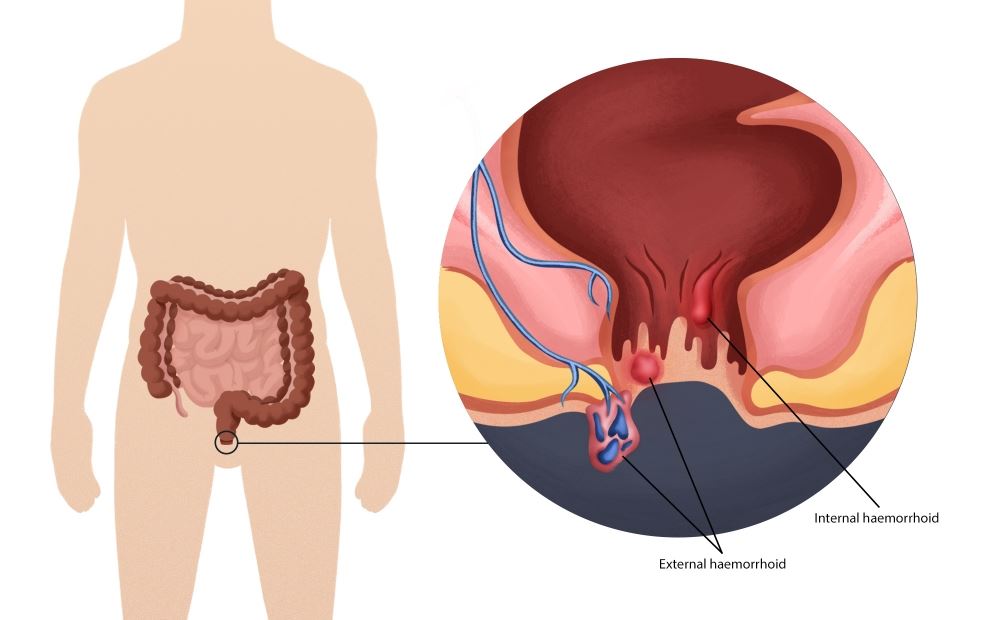
Rectal Bleeding
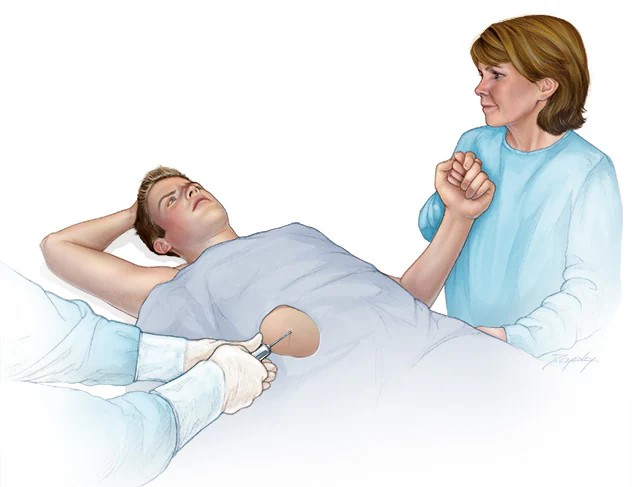
Liver Biopsy Treatment
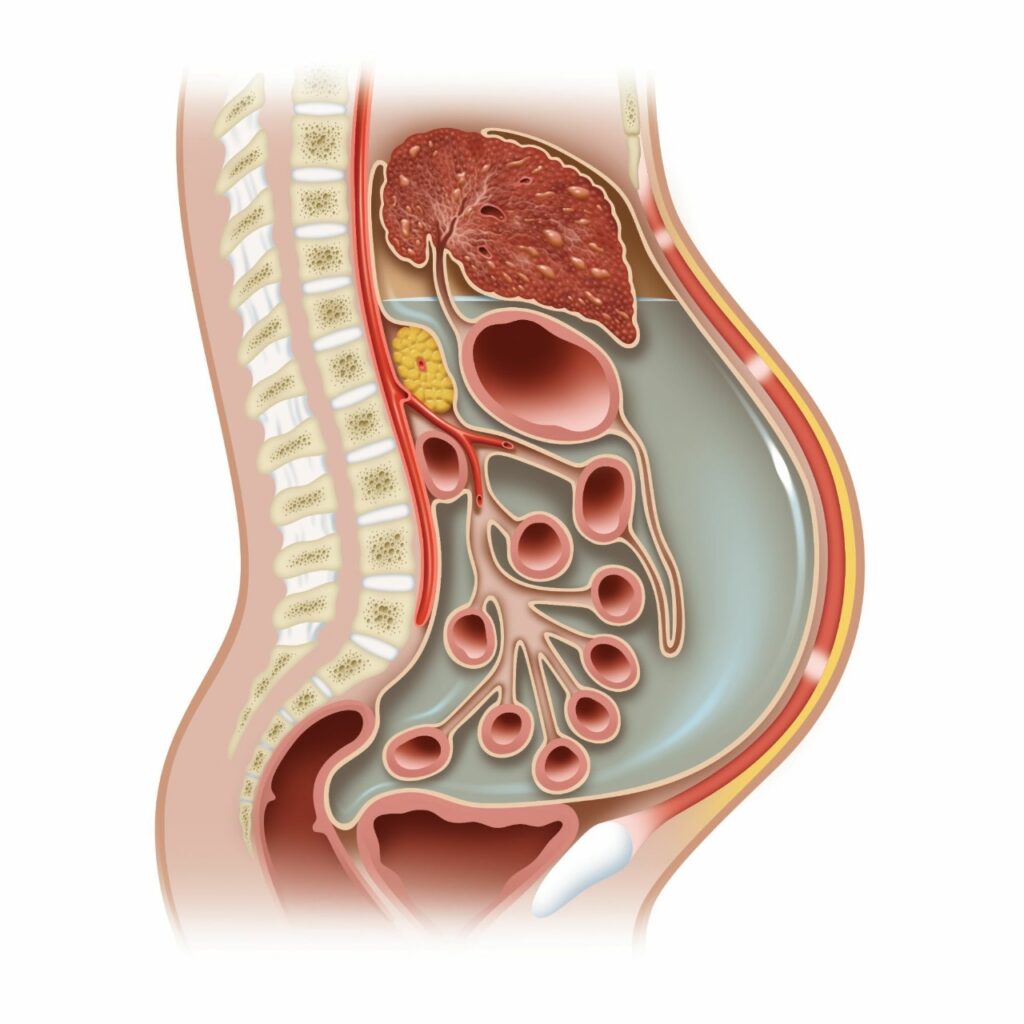
Ascites Treatments
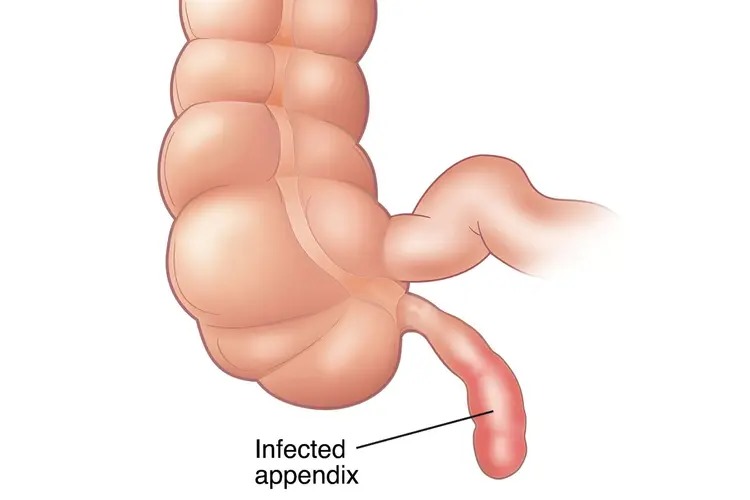
Appendicitis Surgery
Bariatric Surgery
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Surgery
Centre Of Excellence
Dr. G. Ramesh contributes remarkable clinical depth across our Centers of Excellence, strengthening our role in Super Speciality Tertiary Healthcare.

About the Doctor
Dr.Ramesh Gajula – Best Gastroenterologist in Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh
Dr. Ramesh Gajula is a highly skilled and dedicated gastroenterologist in Vijayawada, specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal and liver diseases. Known for his deep medical knowledge and compassionate care, he is recognized among the best gastroenterologist doctors in Vijayawada. With advanced qualifications and years of experience, Dr. Ramesh provides comprehensive treatments for all types of gastric disorders.
As one of the leading liver specialists in Vijayawada, Dr. Ramesh Gajula offers expert care for patients suffering from liver-related diseases. Apart from his clinical excellence, he actively participates in several healthcare initiatives and free medical programs, extending his services to rural and underprivileged communities. His commitment to making quality healthcare accessible to all truly sets him apart.
Listen To Doctor YouTube Shorts
Subscribe For More Videos
Why Choose Dr. Ramesh Gastro And Liver Centre?

Multidisciplinary team of specialists

Advanced endoscopy and laparoscopic theatres

Structured bariatric program with long-term follow-up

24/7 emergency endoscopy services
Doctor Social Media Connect
Doctor Media Connect
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1.What does a medical gastroenterologist do?
A medical gastroenterologist diagnoses and treats disorders of the digestive system (esophagus, stomach, intestines), liver, and pancreas. They perform diagnostic tests like endoscopy, colonoscopy, and manage conditions medically (without surgery).
2.When should I see a gastroenterologist?
If you have persistent abdominal pain, bloating, heartburn, acid reflux, difficulty swallowing, rectal bleeding, chronic diarrhea or constipation, or unexplained weight loss. Also, for liver-related symptoms (jaundice, swelling), or after abnormal blood tests.
3.What are common gastrointestinal conditions treated medically?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Peptic ulcers (sometimes due to H. pylori)
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Liver conditions like fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, hepatitis
Colorectal polyps, early GI cancers.
4.What diagnostic tests are commonly done?
Upper GI endoscopy (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) to look at esophagus, stomach, duodenum.
Colonoscopy for colon/large intestine.
Capsule endoscopy sometimes.
EUS (Endoscopic Ultrasound) for deeper imaging or biopsy.
Functional tests like 24-hour pH monitoring, esophageal manometry.
Breath tests (like hydrogen breath test) for small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) or lactose intolerance.
5.Are gastrointestinal procedures painful?
Most endoscopic procedures (like endoscopy or colonoscopy) are done under sedation, so discomfort is minimal.
Preparation (like bowel cleansing) may be uncomfortable but is manageable.
7.How do I prepare for a procedure like colonoscopy or endoscopy?
Follow the diet restrictions advised by your doctor.
For colonoscopy, bowel preparation (laxatives) will be needed.
Inform your doctor about all medications, especially blood thinners.
Arrange for someone to take you home if sedation is used.
8.How often should I screen for colorectal cancer?
Depends on risk factors: family history, age, prior polyps. (In general, regular screening is recommended.)
Your gastroenterologist will advise based on your personal risk.
9.Can dietary changes help with digestive problems?
Yes — diet modification is often part of treatment. For example, increasing fiber, avoiding trigger foods, reducing fatty/spicy foods, maintaining hydration. Nutrition counselling may be offered.
10.What are the risks of medical GI treatments?
Risks depend on the procedure: bleeding, perforation (rare), infection.
Sedation also carries some risk.
Long-term medications (e.g., proton pump inhibitors) may have side effects and should be monitored.
11.Can lifestyle changes improve my GI health?
Yes. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, reducing stress, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol, maintaining healthy weight all help.
Follow-up with your gastroenterologist for personalized advice.
12.Do I need a second opinion for GI problems?
Yes, especially for complex diagnoses, cancer, or when surgery is being considered. A second opinion can help confirm diagnosis and explore all options.
13.What about cost and insurance?
Costs vary widely depending on the test or treatment. Many hospitals accept health insurance; check with your provider and hospital. For government scheme coverage, check relevant state and central health-insurance schemes.
1.What is surgical gastroenterology?
It deals with surgical treatment of GI tract disorders: stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, biliary tree.
These may include tumor removal, gallbladder surgery, bypass, etc.
2.When is surgery needed for GI problems?
For complications like cancer (stomach, colon), strictures (narrowing), gallstones, appendicitis, hernia, bleeding not managed medically. When medical therapy fails or is not adequate.
3.What are common GI surgeries offered?
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal)
Appendectomy (surgical removal of appendix)
Hernia repair, diagnostic laparoscopy.
Surgeries for GI cancer (e.g., stomach, colon).
Advanced procedures: per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for achalasia.
Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
4.What are the risks associated with GI surgery?
Usual surgical risks: bleeding, infection, anesthesia complications.
Specific risks depend on the type of surgery (e.g., leaks in bowel surgery, strictures).
Recovery time varies.
5.How long is the recovery period after GI surgery?
Depends on procedure: minor laparoscopic surgeries may have shorter hospital stays, faster recovery.
Major surgeries (e.g., cancer resections) may require weeks of recovery.
Follow-up usually includes wound care, diet changes, and monitoring.
6.Does the hospital follow any standard surgical guidelines?
Yes, in India, there are Standard Treatment Guidelines (STGs) for gastrointestinal surgery by the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. These cover diseases like acute pancreatitis, portal hypertension, gallstones, and GI cancers.
7.How do I choose the right gastro-surgeon?
Check their qualifications (MBBS, MS, MCh or equivalent) and experience in GI surgery.
Ask about their experience with the specific surgery you need.
Inquire about minimally invasive vs open surgery options.
8.What should I bring to the hospital for my first surgical consultation?
All previous medical reports, imaging (CT, MRI), endoscopy/colonoscopy reports.
9.Will surgery interfere with daily life and work?
Initially yes — depends on the surgery type and recovery plan.
After recovery, many patients return to normal activities, though there may be some dietary or lifestyle adjustments.
10.Are there less invasive alternatives to surgery?
Yes. Some GI issues may be managed endoscopically (therapeutic endoscopy) rather than open surgery.
Your surgeon/gastroenterologist will discuss options (medical vs endoscopic vs surgery) based on your condition.
11.How do I pay for GI surgery? Insurance, cost, and schemes?
Ask your hospital's billing or insurance cell for cost estimates.
Many private hospitals support cashless treatment under health insurance.
Government schemes (state- or central-level) may cover surgical GI procedures depending on eligibility.
12.What follow-up care is required after GI surgery?
Regular clinic visits to monitor healing, complications.
Diet counseling: may need gradual diet progression (liquid → soft → normal).
Possibly physical activity guidance.
Sometimes repeat imaging or endoscopy, depending on the surgery type.